Deploying RFID Drone technologies requires and understanding of RFID tags first.
RFID tags
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags have been around since the 1940s. Because they enable cost effective identification of objects. The ability to connect everything via the internet is referred to as IOT (Internet of Everything). This number of uniquely identifiable connected objects is expected to reach 45 billion soon.
No built-in power sources are added into passive tags
Readers use radio frequency to power up readers and normally fall into class 0 to 3 range.
The next Class 4 states active tags only which contain their own internal power source to provide energy for specific time period for various operations.
The following Class 5 deals with active tags and readers only that can read data from various tags.
Passive RFIDs
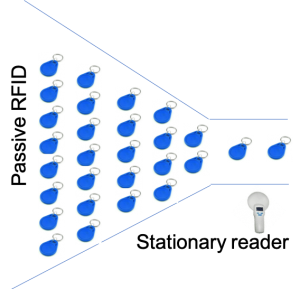
Passive RFID tags have no internal power source and can last a life time. They therefore are inexpensive. Typically ranging from 15 cents to $5 each. Their typical read range is 10m.
As a result these tags are best for high volume assets. Which move uniformly through stationary points of concentration.
Active RFIDs

Active RFID is battery powered with a typical lifespan of 5 years. The read range is 100m+ and they are priced from $15+ each.
Therefore these tags are best for tagging high volume assets. Which move within designated areas in a random and dynamic manner.
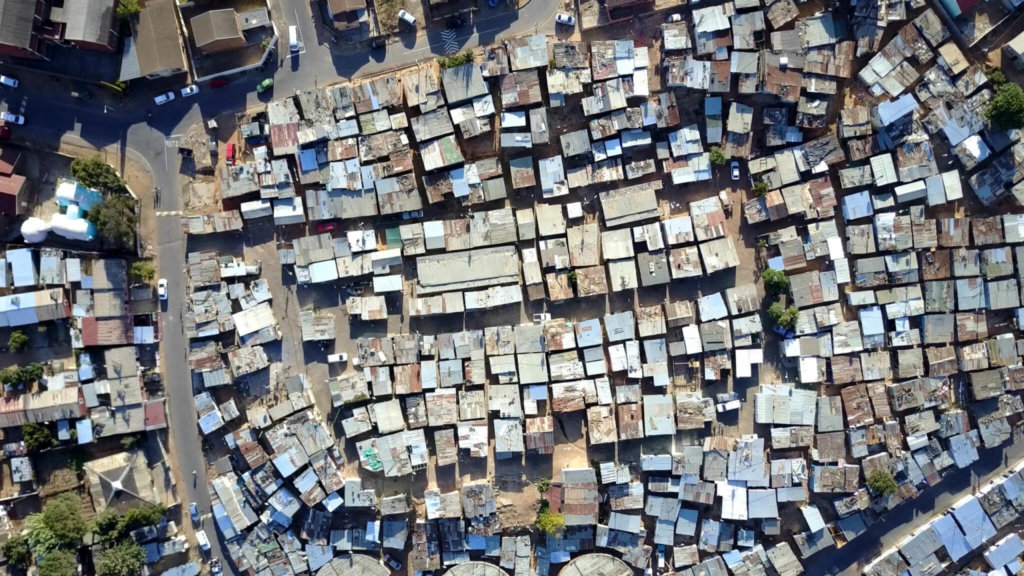
Moving assets: Even cattle farmers on large farms deploy RFID tags and drone based RFID readers with great success.
RFID (IOT) Energy challenge.
The ultimate dream would be to embed active RFID tags in every physical object or asset for reachability. Clearly cost of including such energy capacities on high numbers of tags is an obstacle.
IOT Systems Architecture
The IOT (RFID) Systems Architecture consists of 3 components or layers : Services, Network and Perception.
- Service: This layer transforms the collected data into information content. It then presents the content via a user interface so that it can be consumed by various business processes to be acted upon.
- Network:The network layer is responsible for efficient and reliable infrastructure. This is to support the service layer and the large scale industrial applications it supports
- Perception: This where the data and information about objects existing in the physical world are being collected via a variety of sensors and RFID tags
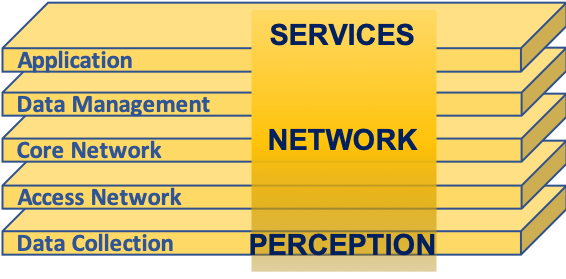
The RFID Systems Architecture is aligned with, and underpinned by, the internationally adopted OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Model. The OSI Model characterises and standardises the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to its underlying internal structure and technology.
RFID Applications
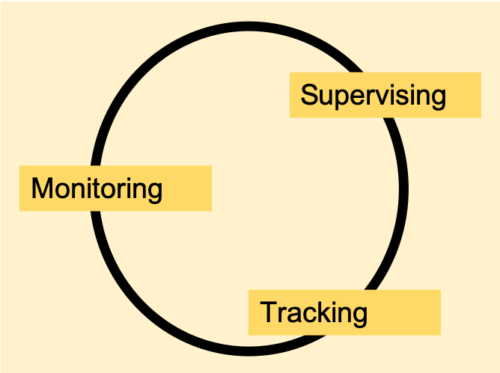
The RFID functions consists of 3 categories: Monitoring, Tracking and Supervising.
- Monitoring concerns itself with that latest situation of the system – looking for any signs of abnormal behaviour,
- Tracking provides observation of the object while on the move and
- Supervising is concerned with the activities or behaviour of the system.
Some use cases for UAV based networking applications
- Provide energy-efficient and reliable IoT uplink connections.
- Cache popular content and efficiently serve mobile users by following their mobility patterns.
- Act as users of the wireless infrastructure for surveillance, remote-sensing.
Technology roadmap for RFID and IOT.
The RFID and IOT is increasingly becoming more and more ubiquitous in everyday life. The technology roadmap below provides an outline of its progression.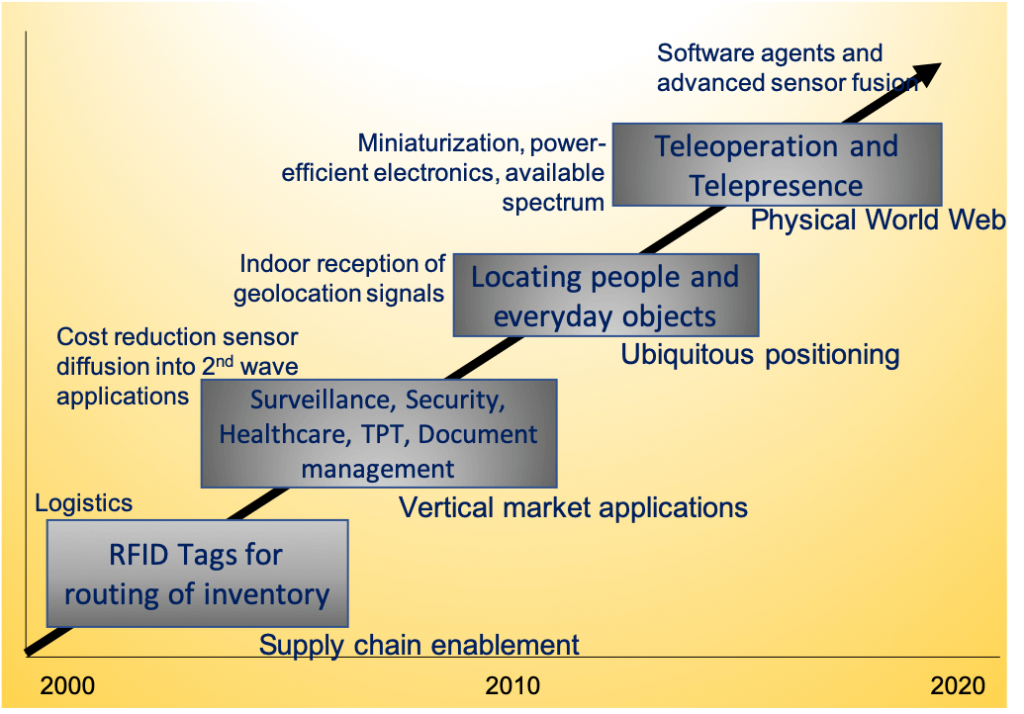
Communication is very important when deploying UAVs. The following categories of communication technologies are available to UAVs. The first 3 (highlighted) are the most effective when using UAVs to compliment RFIDs.
|
Category |
Technology |
Data Rate |
Range |
Latency |
|
WPAN “ WLAN |
Bluetooth 4.0 Zigbee 802.11a/b/g/n/ac |
<1 Mbps <250 kbps <600 Mbps |
60 m <100 m <250 m |
50 50 75 |
|
WLAN LPWA “ Cellular “ “ “ “ |
WAVE 802.11p LoRA SigFox NB-IoT LTE-ML TE Advanced (4G) LTE D2D 5G |
<27 Mbps <50 kbps <100 bps <250 kbps <1 Mbps <1 Gbps – <10 Gbps |
<1 km <15 km <20 km World wide “ “ “ “ |
50 82 82 75 75 50 25 3 |
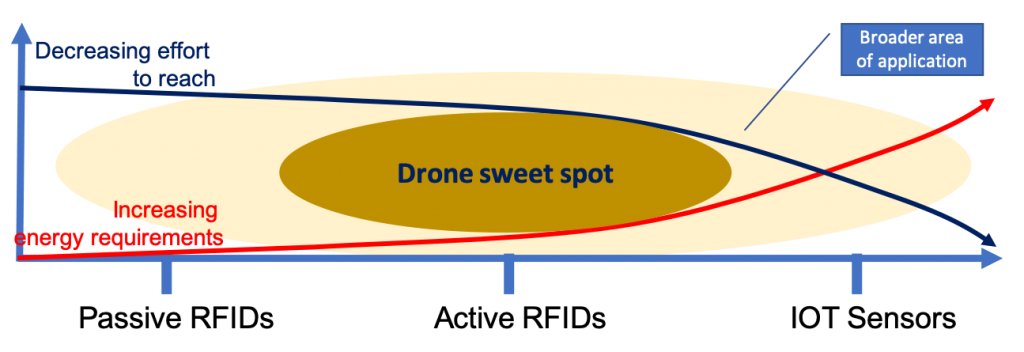
One of the hottest technology trends for 2019 and is 5G wireless networking. Other than extremely fast with very high data rates, the wireless network also operates with 90% less energy. However, until 5G arrives the energy gap remains the main obstacle with the deployment with RFID (and IOT).
For now, the range and reach of drone based RFID readers fits the energy gap (see diagramme) gap perfectly. The RFID (IOT) environment, consist of participating devices with very limited sources of energy. As a result, rotary drones can be efficiently and dynamically positioned to allow RFID (IOT devices) to transmit with minimum power.
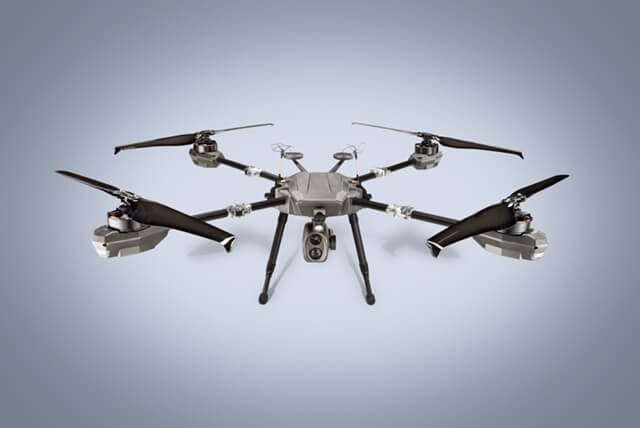
RFID Drone Platforms
The Airborne Drones Vanguard has a flight range of 60 – 90 minutes. This allows the Vanguard is able to carry payloads that include multiple sensors which incorporates a RFID reader with ease. Advanced onboard systems enable advanced networking and onboard processing. As a result this makes the Vanguard a compelling solution. It has the range and reach to overcome the energy challenges RFID-based asset management requirements.